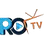Exploring the realms of Functional health vs conventional medicine sheds light on contrasting healthcare paradigms that shape our understanding of wellness and treatment methodologies. As we delve into this discourse, a nuanced perspective emerges, unveiling the intricate interplay between personalized care and traditional medical approaches.
Functional Health vs Conventional Medicine
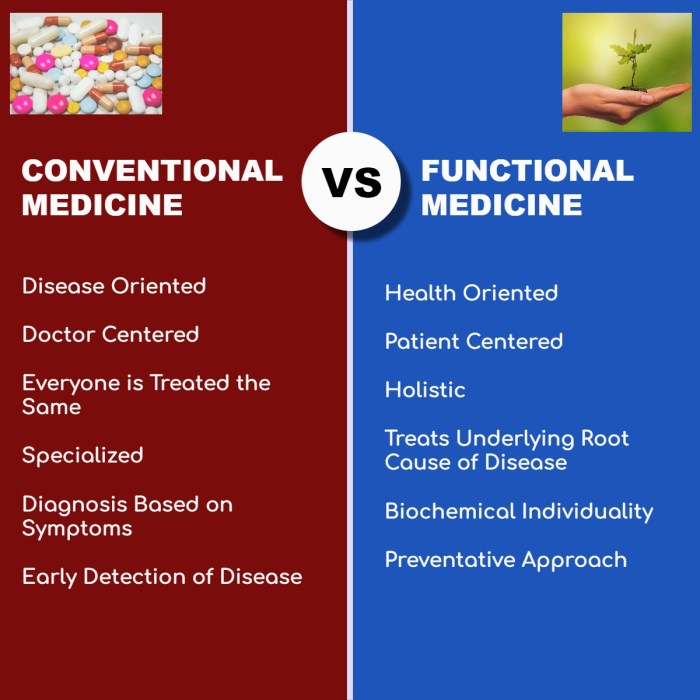
Functional health focuses on addressing the root causes of illness and disease, emphasizing prevention and proactive approaches to healthcare. It considers the interconnectedness of the body's systems and aims to optimize overall well-being. On the other hand, conventional medicine, also known as allopathic medicine, typically treats symptoms of a disease or condition using pharmaceuticals, surgeries, and other interventions.
Core Principles and Approaches of Functional Health
Functional health is centered around personalized, holistic care that takes into account an individual's lifestyle, genetics, environment, and unique health history. Practitioners of functional health often use a combination of nutrition, exercise, stress management, and supplements to support the body's natural healing processes.
The focus is on treating the whole person, not just the symptoms.
Historical Background and Evolution of Conventional Medicine
Conventional medicine has its roots in ancient healing practices and has evolved over centuries to incorporate scientific advancements and technological innovations. The rise of pharmaceuticals and evidence-based medicine has become central to the practice of conventional medicine, with a focus on diagnosing and treating specific diseases rather than promoting overall wellness.
Differences in Treatment Philosophies
Functional health and conventional medicine differ in their approaches to treatment. While conventional medicine tends to rely on medications and surgeries to manage symptoms, functional health seeks to identify and address the underlying imbalances that contribute to illness. Functional health practitioners often emphasize the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, in promoting long-term health and wellness.
The Role of Prevention
Preventive care plays a crucial role in both functional health and conventional medicine, but their approaches differ significantly.
Comparison of Preventive Care Approaches
- Functional health focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of health issues before they manifest into diseases. This approach emphasizes proactive steps to maintain overall well-being.
- Conventional medicine, on the other hand, often relies on reactive measures such as screenings and tests to detect diseases after symptoms appear, leading to a more disease-centered approach.
Preventive Strategies in Functional Health
Functional health practices employ various preventive strategies to promote long-term health and wellness.
- Personalized nutrition plans tailored to individual needs, focusing on nutrient-dense whole foods and avoiding processed ingredients.
- Regular physical activity routines that suit one's fitness level and preferences to support overall health and prevent chronic conditions.
- Stress management techniques like mindfulness meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to reduce the impact of stress on the body.
Emphasis on Lifestyle Factors in Preventing Diseases within Functional Health
Functional health places a strong emphasis on lifestyle factors as key determinants of health outcomes
- Encouraging healthy sleep habits to support optimal rest and recovery, crucial for maintaining a robust immune system and overall well-being.
- Promoting social connections and emotional well-being as integral parts of a holistic approach to health, recognizing the impact of relationships on mental and physical health.
- Advocating for regular physical activity not just for weight management but also for improving cardiovascular health, reducing inflammation, and enhancing overall vitality.
Treatment Modalities
Functional health takes a comprehensive approach to treatment, focusing on addressing the root causes of illness through personalized plans that include nutrition, stress management, and exercise. This contrasts with conventional medicine's reliance on pharmaceuticals for symptom management rather than addressing underlying issues.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays a crucial role in functional health, with a focus on using food as medicine to prevent and treat various health conditions. Functional health practitioners often recommend personalized dietary plans based on an individual's unique needs, aiming to optimize overall health and well-being.
Stress Management
Stress management is another key component of functional health, as chronic stress can have a significant impact on overall health. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and breathing exercises are commonly used to help individuals reduce stress levels and improve their resilience to stressors.
Exercise
Exercise is considered a fundamental pillar of functional health, with physical activity playing a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Functional health practitioners often prescribe individualized exercise programs tailored to a person's specific health goals, focusing on improving strength, flexibility, cardiovascular health, and overall well-being.
Integrative Approaches
Functional health emphasizes integrative approaches that combine various treatment modalities to address the root causes of illness. By considering the interconnectedness of the body systems and factors contributing to disease, functional health practitioners create personalized treatment plans that may include a combination of nutrition, stress management, exercise, supplements, and other natural therapies.
Patient-Centered Care
Functional health and conventional medicine approach patient care differently, with functional health placing a strong emphasis on individualized care and empowerment.
Role of the Patient in Decision-Making
In functional health practices, patients are actively involved in the decision-making process regarding their health. They are encouraged to take charge of their well-being by participating in discussions about treatment options, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures. This collaborative approach ensures that the patient's preferences, values, and goals are taken into consideration when creating a personalized healthcare plan.
Symptom Management vs Holistic Care
Conventional medicine often focuses on managing symptoms through medications or procedures without always addressing the underlying causes of health issues. In contrast, functional health looks at the whole person and aims to identify and treat the root causes of illness, taking into account the interconnectedness of body systems and environmental factors.
This holistic approach often leads to more sustainable long-term health outcomes for patients.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the juxtaposition of Functional health and conventional medicine unveils a spectrum of perspectives that redefine patient care and treatment modalities. By embracing the essence of individualized wellness and holistic approaches, we pave the way for a future where health is not just a destination but a transformative journey towards well-being.
FAQ Explained
How does functional health differ from conventional medicine?
Functional health focuses on addressing root causes of illness through personalized treatment plans, while conventional medicine often relies on symptom management and standardized approaches.
What preventive strategies are commonly used in functional health practices?
Functional health emphasizes lifestyle factors like nutrition, stress management, and exercise as preventive strategies to maintain overall well-being.