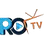Delving into the realm of electric car charging technologies reveals a landscape filled with innovation and efficiency. From plug-in systems to wireless solutions, the evolution of charging methods for electric vehicles is both fascinating and crucial for the future of sustainable transportation.
Overview of Electric Car Charging Technologies
Electric vehicles are becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable mode of transportation, leading to a growing need for efficient charging technologies. There are several types of electric car charging technologies available in the market, each offering different charging speeds and compatibility with various electric vehicle models.
Types of Electric Car Charging Technologies
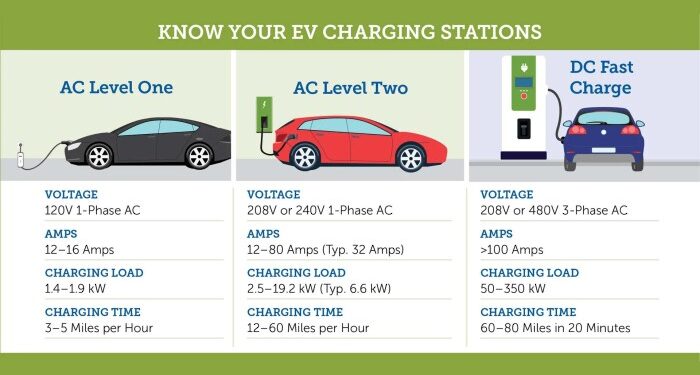
- Level 1 Charging: This involves using a standard 120-volt household outlet, providing a slow charging rate suitable for overnight charging.
- Level 2 Charging: Utilizing a 240-volt outlet, level 2 chargers offer faster charging speeds compared to level 1 chargers, making them ideal for home charging stations and public charging stations.
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): DC fast chargers deliver a high-power DC charge directly to the vehicle's battery, allowing for rapid charging sessions typically found at public charging stations along highways.
Importance of Efficient Charging Technologies
Efficient charging technologies play a crucial role in the adoption of electric vehicles by providing convenience, reducing charging times, and ensuring compatibility with a wide range of electric vehicle models. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise, the development of fast and reliable charging solutions becomes increasingly essential to support widespread electric vehicle use.
Comparison of Charging Technologies
| Charging Technology | Charging Speed | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Slow | Home charging |
| Level 2 | Medium | Home and public charging |
| DC Fast Charging (Level 3) | Fast | Highway charging |
Plug-in Charging Systems
Electric vehicles rely on plug-in charging systems to recharge their batteries. These systems allow the car to connect to an external power source, such as a charging station or a wall outlet, to replenish the energy needed to operate.
Different Plug Types
There are several types of plugs used in electric car charging, each with its own specifications and compatibility. Some of the common plug types include:
- J1772: This plug type is widely used in North America and Japan, known for its safety features and reliability.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): CCS plugs can support both AC and DC charging, making them versatile and efficient.
- CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO plugs are primarily used for fast charging and are common in Asian and European markets.
- Tesla Supercharger: Tesla vehicles use their proprietary Supercharger plug, designed for fast charging exclusively for Tesla cars.
Evolution of Plug-in Charging Systems
Over the years, plug-in charging systems have evolved significantly to meet the growing demands of electric vehicles. The advancements include:
- Increased charging speeds: Newer plug-in systems can deliver higher power levels, reducing charging times significantly.
- Standardization efforts: Industry-wide efforts have been made to standardize plug types and charging protocols for better compatibility and convenience.
- Wireless charging technology: Research and development are ongoing to implement wireless charging solutions, eliminating the need for physical plugs altogether.
- Smart charging capabilities: Modern plug-in systems often come equipped with smart features, such as scheduling charging times or monitoring energy consumption remotely.
Wireless Charging Technologies
Wireless charging technologies for electric cars operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. This involves transferring energy from a charging pad on the ground to a receiver pad located on the underside of the vehicle, without the need for physical cables.
Efficiency Comparison
Wireless charging offers the convenience of simply parking over a charging pad without the hassle of plugging in a cable. However, this convenience comes at a cost in terms of efficiency. Wired charging systems are typically more efficient as they have a direct connection, resulting in faster charging times and less energy loss during the charging process.
- Wireless charging systems can be less efficient due to energy loss during the transmission of power over a distance.
- Wired charging systems offer faster charging times and are generally more energy-efficient.
- Efficiency can vary based on the specific technology and implementation of wireless charging systems.
Challenges and Future Prospects
While wireless charging technologies offer a promising solution for electric vehicle charging, there are several challenges that need to be addressed for wider adoption.
- Cost: Wireless charging systems can be more expensive to install compared to traditional wired charging infrastructure.
- Standardization: The lack of a universal standard for wireless charging technologies can hinder interoperability between different vehicles and charging stations.
- Efficiency: Improving the efficiency of wireless charging systems to reduce energy loss during power transfer is essential for their long-term viability.
- Future Prospects: Advances in technology and ongoing research may lead to more efficient and cost-effective wireless charging solutions in the future, driving increased adoption of this technology.
Fast Charging Solutions
Fast charging solutions for electric vehicles have revolutionized the way we charge our cars, offering rapid charging times that enable drivers to get back on the road quickly. Let's explore the concept of fast charging, popular standards in the market, and its impact on battery life and performance.
Popular Fast Charging Standards
There are several fast charging standards used in the market today, each offering different charging speeds and compatibility. Some popular fast charging standards include:
- CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO is known for its fast charging capabilities and is commonly used by Japanese automakers.
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Widely adopted in Europe and North America, CCS combines AC and DC charging, offering high power levels for faster charging.
- Tesla Supercharger: Exclusive to Tesla vehicles, the Supercharger network provides rapid charging speeds for Tesla owners, making long-distance travel more convenient.
Impact of Fast Charging on Battery Life and Performance
While fast charging offers the convenience of quick charging times, it can also have an impact on battery life and overall performance of electric vehicles. Rapid charging generates more heat and stress on the battery, which can lead to faster degradation over time.
Manufacturers are continuously working on improving battery technology to mitigate the effects of fast charging and ensure long-term durability.
Smart Charging Infrastructure
Smart charging infrastructure refers to the advanced technology and network systems designed to optimize the charging process for electric vehicles. These systems utilize a combination of IoT (Internet of Things) and connectivity to efficiently manage and control the charging of electric cars.
Role of IoT and Connectivity
IoT plays a crucial role in smart charging infrastructure by enabling real-time communication between electric vehicles, charging stations, and the grid. Through IoT sensors and data analytics, smart charging networks can monitor the energy demand, grid capacity, and vehicle charging status to ensure optimal charging efficiency.
- IoT sensors enable remote monitoring of charging stations and allow for predictive maintenance to prevent downtime.
- Connectivity facilitates communication between electric vehicles and charging stations, enabling dynamic charging rates based on grid conditions and energy prices.
- Smart charging infrastructure can prioritize charging for vehicles with urgent needs or those requiring a specific amount of charge within a set timeframe.
Examples of Smart Charging Solutions
One example of a smart charging solution is Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology, which allows electric vehicles to not only charge from the grid but also discharge energy back to the grid when needed. This bi-directional energy flow helps balance the grid and reduce peak demand.Another example is Demand Response (DR) programs, where electric vehicle owners can receive incentives for adjusting their charging schedules based on grid conditions.
By participating in DR programs, electric vehicle owners can contribute to grid stability and energy efficiency.Overall, smart charging infrastructure enhances the flexibility, efficiency, and sustainability of electric vehicle charging, paving the way for a more interconnected and intelligent transportation ecosystem.
Last Point
In conclusion, the world of electric car charging technologies is vast and dynamic, offering a glimpse into the future of transportation. As advancements continue to push boundaries, the possibilities for efficient and eco-friendly charging solutions are endless.
Commonly Asked Questions
Are wireless charging technologies as efficient as wired charging?
Wireless charging technologies are rapidly improving in efficiency, but currently wired charging remains slightly more efficient.
How does fast charging impact the overall performance of electric vehicle batteries?
Fast charging can increase the rate of battery degradation over time, affecting the overall lifespan of the battery.
What role does IoT play in smart charging networks for electric cars?
IoT enables smart charging networks to optimize charging schedules based on energy demand, grid capacity, and vehicle usage patterns.